blog
Consent Management: The Key to Building Patient Trust
SECTIONS
A shift from traditional harm prevention to proactive rights protection is underway in a growing number of U.S. state data privacy regulations. In 2023, Colorado, Connecticut, Utah, and VirginiaOpens in a new tab will join California in passing new statutes modeled after the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). These laws effectively grant individuals legal ownership of their personal data.
For healthcare organizations, achieving and maintaining compliance with new regulations hinge on using consent management to build trust with patients.
In this guide, you’ll learn what consent management is and how informed consent empowers patients to have more control over their personal data.
Key Takeaways:
- Many new patient data privacy regulations will go into effect in the U.S. this year.
- Consent management in healthcare is vital for complying with new regulatory controls and empowering patients to make informed decisions regarding their treatment and the sharing of their private health information.
- Proactive consent management practices help healthcare organizations build patient trust.
What Is Consent Management?
In healthcare, consent management refers to the process of obtaining, documenting, and managing patients’ informed consent for medical treatment, procedures, and the sharing of their health information. The purpose of consent management is to give patients the autonomy to make informed decisions about their healthcare while protecting their private information from misuse and exposure.
In healthcare contexts, consent management happens in three phases:
- Providing information: Healthcare providers must provide patients with sufficient information about their conditions, treatment options, potential risks and benefits, and any alternatives available. Providers need to present this information clearly, accounting for patients’ language proficiencies, cultural backgrounds, and any other factors that may impact their comprehension. Patients must have the opportunity to ask questions and seek clarification before deciding.
- Obtaining consent: Patient decisions regarding treatment require documentation in consent forms. Consent forms must describe procedure details, potential risks and complications, and expected outcomes.
- Managing patient data: Healthcare providers must exchange patient data with other entities to ensure continuity of care. However, patients must always provide explicit consent based on full disclosure of the purpose, scope, and recipients of the data sharing.
5 Ways to Foster Patient Trust with Consent Management
Here are five ways healthcare organizations can build patient trust with consent management.
1. Implement Transparent Consent Processes
Informed consent requires transparent processes that help patients understand their conditions and treatment options. Healthcare providers should develop processes that communicate health information clearly to people of all backgrounds and understanding levels.
To facilitate patient understanding, providers can use educational materials such as brochures, visual aids, videos, and online resources. Multimedia materials can simplify complex concepts, providing patients with a clear understanding of potential risks, benefits, and personal commitments of various treatment options.
Providers can further enhance transparency through open dialogue with patients, actively seeking their input on treatment and data sharing choices.
2. Securely Manage Patient Data
The surge in data breaches and unauthorized access to private patient information has heightened concerns about privacy and data security. In the second half of 2022, breached patient records in healthcare organizations rose 35%Opens in a new tab over the prior year, from 21.1 million records in 2021 to 28.5 million records.
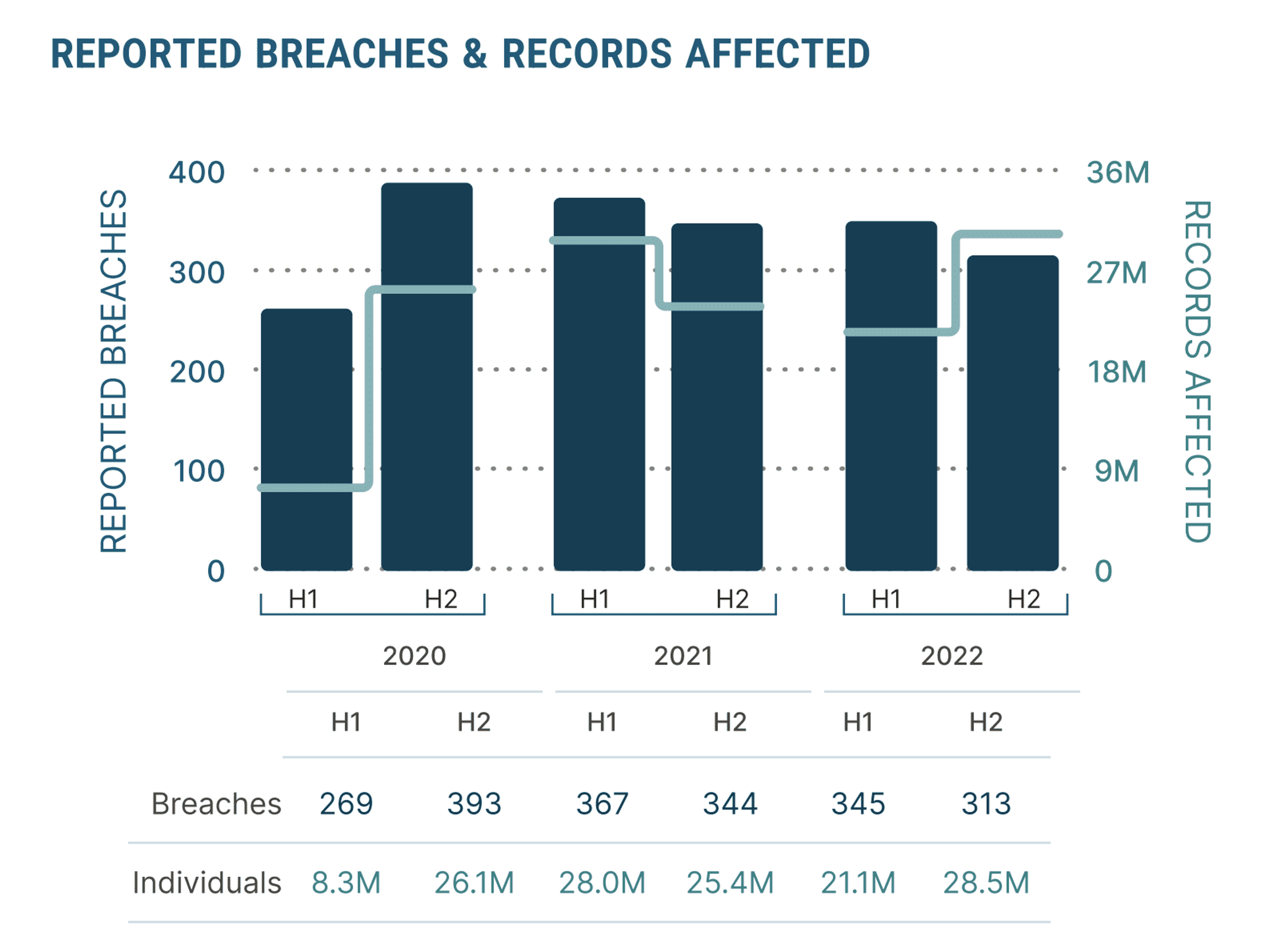
Image Source: Hubspot
Organizations can build trust by transparently communicating their data management practices to patients upfront. These practices should include strong encryption protocols, multifactor authentication, access controls, and regular security audits. Additionally, organizations must provide patients with the tools to withdraw consent for the storage or sharing of previously disclosed information.
3. Provide Opt-Out Options for Data Sharing
The rights-based consent management approach being adopted by states emphasizes patient control over sharing of their health information. In recent years, a lack of transparency in healthcare data sharing practices has led to an alarmingly high rate of unapproved data disclosures to third parties by healthcare organizations.
Image Source: Scribd
A 2022 study found that 98.6%Opens in a new tab of hospital websites contained third-party tracking software for undisclosed transfer of data to tech service providers, social media companies, advertising firms, and data brokers.
Several patients have brought legal action against hospitals after being informed, resulting in punitive settlements. Organizations can avoid these outcomes and adhere to new state regulations by requesting explicit consent for all personal information disclosures and offering clear opt-out options.
4. Educate Patients about Consent Rights
Many patients are unaware of their rights under both new and previous regulations and how much control they can exert over their healthcare decisions and personal health information. Organizations that address gaps in patient understanding proactively with educational initiatives at various points of care can foster improved patient trust.
To guarantee informed consent, organizations should make patient rights information available in waiting room materials, patient portals, and marketing contentOpens in a new tab. For patients seeking more detailed legal and ethical perspectives, healthcare providers can hold informational sessions or webinars dedicated to explaining consent management.
5. Create Positive Patient Experiences through Open Dialogue
Recent studiesOpens in a new tab suggest patients care less about the kind of personal information healthcare organizations share for care purposes than they do about feeling well-informed and treated respectfully – i.e., without stigma or discrimination. The more providers involve patients in open, ongoing dialogue, the better they can understand nuanced consent preferences and enable patient autonomy in data-sharing decisions.
In practice, this dialogue must regularly occur throughout the cycle of care. Healthcare organizations should establish channels for patients to express their concerns and implement feedback systems such as patient satisfaction surveys, suggestion boxes, and online forums.
Healthcare Master Data Management with Coperor by Gaine
Coperor’s master data management platform specifically serves the needs of the healthcare and life sciences industries. With an adaptable data model tailored for healthcare data management applications, Coperor enables comprehensive data integration across complex organizations and their partner networks.
To learn more about Coperor, watch this demo and contact our team today.