blog
How (and When) to Use External Data Providers
SECTIONS
Data is a pivotal factor in driving innovation, research, and quality patient care in modern healthcare and life sciences industries. Amidst this data-driven revolution, external data providers have emerged as vital contributors, offering insights that go beyond the reach of average internal data capabilities.
For many organizations looking to enhance their data strategies and capabilities, the question of whether or not to use external data providers is a timely one. In this article, we’ll help you evaluate the possibility in detail.
We’ll start by providing an overview of external data providers and what they do, then explore strategic use cases in which they’re beneficial and how to find the right provider for your unique organization. When you’re done reading, you’ll have a full understanding of the opportunity and be equipped with the knowledge you need to make the best decision for your business.
Key Takeaways:
- External data providers supply data collected from sources outside an organization’s internal systems, including public health and research databases.
- Important use cases for external data providers include to inform research, manage public health, improve patient care, and enhance compliance.
- Reputation, data quality, integration capabilities, compliance, and cost are all important factors when considering external data providers for your organization.
What Are External Data Providers and Why Are They Valuable?
External data providers in healthcare and life sciences are entities or resources that supply data collected outside an organization’s internal systems. These providers range from public health databases and clinical research organizations to commercial data vendors and patient registries. They offer diverse data sets from across relevant ecosystems.
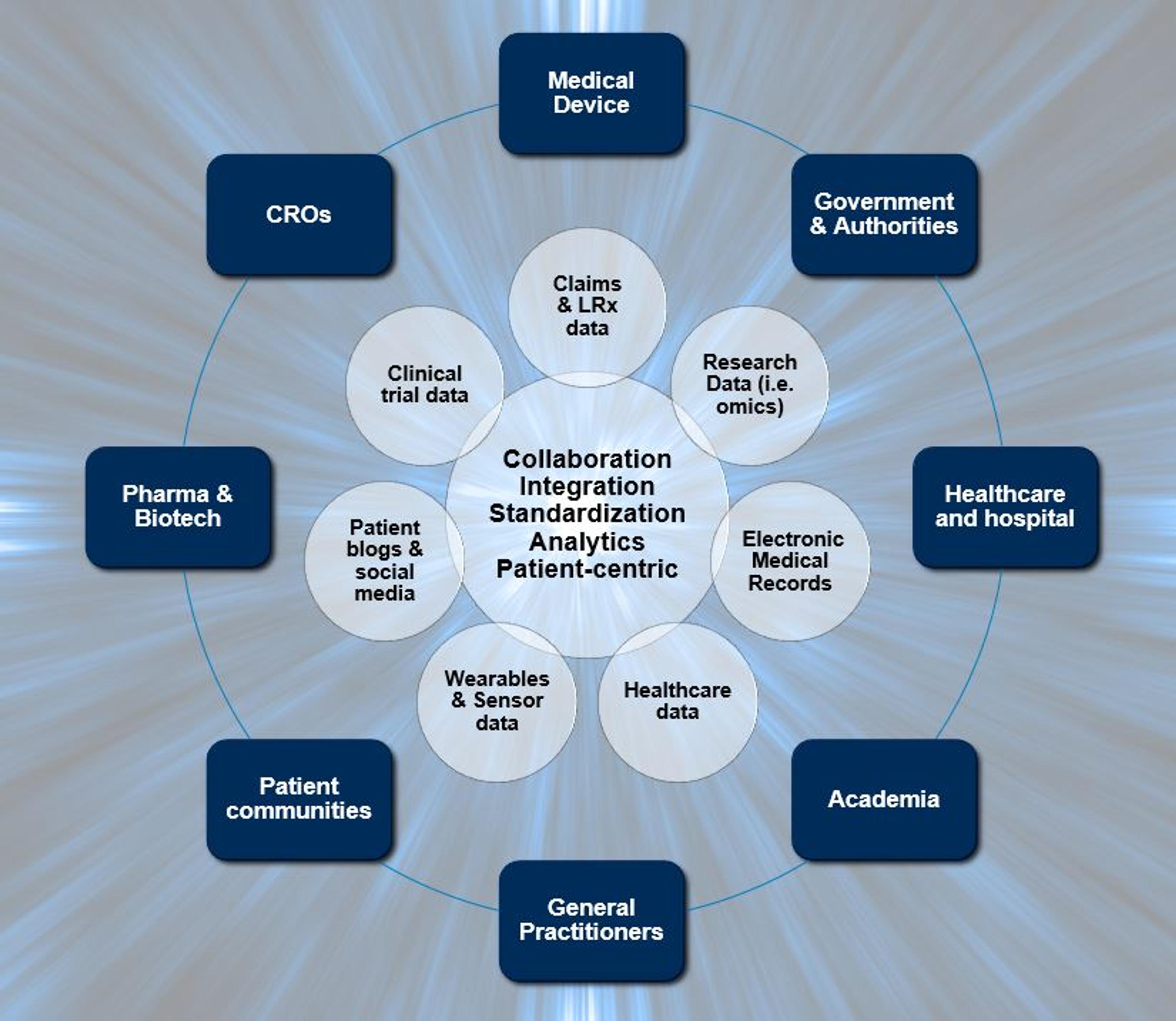
Image Source
The value of these external data sources lies in their ability to complement and enhance internal datasets. Healthcare organizations possess extensive data that includes patient records and operational processes, but this data might be limited in scope.
External data providers bridge this gap, offering broader perspectives and deeper insights that can be pivotal for comprehensive patient care and advanced research.
Incorporating external data can provide a more complete picture of patient populations, disease trends, and treatment efficacies. For instance, clinical trial data from external sources can offer benchmarks and comparative insights that are invaluable for new drug development or therapy assessments.
Similarly, population health data can assist in identifying unmet medical needs or in tailoring healthcare services to specific demographic groups.
Moreover, external data can validate and strengthen internal findings, ensuring robustness in research conclusions and clinical decisions. In scenarios where internal data presents certain limitations—such as rare disease research or emerging medical technologies—external data is a key asset in expanding knowledge and guiding decision-making.
The integration of external data into healthcare practices also aligns with the broader shift towards evidence-based medicine. It facilitates informed decisions, supports personalized healthcare strategies, and ultimately leads to better health outcomes.
As a result, the strategic use of external data providers has become more than a supplementary aspect of healthcare operations and is now a competitive imperative for many organizations.
When to Utilize External Data Providers
Determining when to utilize external data providers requires a strategic assessment of organizational needs, data gaps, and the specific objectives at hand. Healthcare and life sciences organizations should consider external data in these key scenarios:
Enhancing Research and Development
In the arena of research and development, especially in drug and treatment discovery, leveraging external data can be transformative. This data offers insights into broader patient demographics, varying disease progression patterns, and outcomes from previous clinical studies, which may not be available within an organization’s internal data.
Such information is invaluable for identifying unmet medical needs, understanding the efficacy of existing treatments, and pinpointing potential areas for innovation. By integrating these external insights, healthcare organizations can significantly enhance the effectiveness and accuracy of their research, leading to groundbreaking discoveries and more effective treatments.
Population Health Management
Managing the health of larger populations effectively requires a comprehensive understanding that often surpasses the scope of internal data. External data provides a broader perspective, offering insights into epidemiological trends, health behaviors, and the impact of social determinants on community health.
This data helps healthcare organizations identify high-risk populations, tailor public health initiatives, and allocate resources more effectively. By utilizing this expansive data, healthcare providers can develop more targeted interventions, predict and prevent disease outbreaks, and contribute to improved health outcomes for entire communities.
Improving Patient Care
External data is particularly valuable in enhancing personalized patient care. It offers additional context and insights that enrich a patient’s medical history and response to treatments, especially in the case of rare or complex conditions.
This data can include patient experiences with similar conditions, outcomes from alternative treatments, or insights into genetic markers. Such comprehensive information enables healthcare providers to tailor care plans more accurately to individual patient needs, anticipate potential complications, and optimize treatment strategies.
Consequently, the integration of external data into patient care leads to more informed decision-making, personalized treatment approaches, and overall improved patient outcomes.
The opportunity to leverage personalization as a patient engagement enhancer is significant today—75% of patients want deeper personalizationOpens in a new tab in their healthcare, and 61% would visit their provider more often if their communications and experiences were personalized. This has huge implications for patient adherence and outcomes.

Image Source
Regulatory Compliance and Reporting
Adhering to regulatory compliance and achieving accurate reporting in healthcare often requires benchmarking against broader industry standards, for which external data is essential. This data provides comparative insights that help healthcare organizations align with regulatory norms and best practices.
It also plays a crucial role in performance measurement, quality assurance, and outcome reporting. By leveraging external data, organizations can ensure they meet legal and ethical standards, avoid penalties, and maintain high levels of patient care quality.
It also aids in transparent reporting, reinforcing the organization’s commitment to regulatory compliance and excellence in healthcare delivery.
How to Choose the Right External Data Providers
Selecting the right external data providers is a critical decision that can significantly impact the efficacy of data-driven initiatives in healthcare and life sciences. Here are some of the important criteria to consider when choosing a provider:
- Reliability and Reputation: Evaluate the track record and credibility of the data provider. Reputable sources with a history of accuracy and reliability are essential.
- Data Quality: Comprehensively assess data quality, including its accuracy, completeness, and relevance. High-quality data is free from errors, biases, and is up-to-date.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensure that the data provider adheres to all relevant healthcare regulations, including data privacy laws like HIPAA or GDPR. Compliance is non-negotiable in healthcare data management.
- Scope and Specialty: Consider the provider’s area of expertise and the scope of their data offerings. Providers should align with your specific data needs, whether it’s detailed patient health data, epidemiological trends, or specific disease-related information.
- Integration Capabilities: The provider’s data should be easily integrable with your existing systems. Evaluate the compatibility of data formats, the ease of integration, and the potential need for additional tools or software.
- Cost and Value Proposition: Consider the cost of acquiring data from the provider and weigh it against the potential value it brings to your organization. The investment should align with the expected outcomes and benefits.
By carefully assessing these factors, healthcare organizations can choose external data providers that not only meet their data needs but also contribute to enhancing overall healthcare delivery and research.
Integrating External Data into Healthcare Systems
Integrating external data into existing healthcare systems is a complex process that requires careful planning and execution. Best practices include:
- Ensuring Data Compatibility: Check that the external data is in a format that can be easily integrated into your current systems. This may involve data conversion or the use of middleware for seamless integration.
- Maintaining Data Privacy and Security: Implement robust security measures to protect data privacy and integrity. This includes encrypting data transfers and ensuring secure storage.
- Developing a Standardized Process: Establish clear protocols for data integration, including validation checks, quality control measures, and audits to ensure data integrity and accuracy.
- Training Staff: Educate your team on how to handle and utilize the new data effectively. This includes understanding how to interpret the data and integrate it into clinical or operational decision-making processes.
Successful integration of external data can lead to improved patient outcomes, more informed research, and better decision-making across healthcare organizations.
Putting it All Together
External data providers play an increasingly crucial role in the healthcare and life sciences sectors, offering invaluable insights and augmenting internal data capabilities.
By understanding when and how to effectively utilize these providers, healthcare organizations can significantly enhance their data strategies and achieve better business, patient, research, and public health outcomes., patient care, and operational efficiency.
To successfully access and integrate data from external data providers, you need to have a high-quality data management tool in place. Gaine’s Coperor platform is a highly scalable and ecosystem-wide master data management solution specifically designed for the unique challenges of the healthcare and life sciences industries.
To learn how Coperer can help your organization transform, start your real-time demo today.