blog
How to Track Patient Adherence and Preference
SECTIONS
In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, patient-centered care has become a guiding principle. Central to this approach are two crucial aspects: patient adherence and preference.
These factors play pivotal roles in shaping treatment plans and patient satisfaction. As healthcare continues to embrace personalized approaches, tracking patient adherence and preference has become essential to achieving positive patient outcomes.
In this article, we’ll explore exactly what patient adherence and preference tracking entails, effective ways to do it, and how a quality master data management tool can enhance your capabilities.
Key Takeaways:
- Patient adherence is the extent to which a patient follows their treatment plan, and preference is their unique inclinations, choices, and priorities.
- Both adherence and preference alignment are essential for achieving positive patient outcomes.
- Effective ways to track patient adherence include self-reported patient diaries, surveys, mobile apps, wearable devices, and EHRs.
- Master data management (MDM) tools centralize, standardize, and automate healthcare data management to make adherence and preference tracking more effective.
What is Patient Adherence and Preference?
Patient Adherence
In the context of healthcare, patient adherence refers to the degree to which patients follow their prescribed treatment regimens as outlined by their healthcare providers. This regimen can encompass many aspects including medication schedules, dietary modifications, exercise routines, and follow-up appointments.
Adherence is not solely about following instructions, however. It’s also a reflection of the patient’s ability and available resources to follow medical recommendations successfully and incorporate them into their daily lives.
There are five dimensions to patient adherence that, collectively as a framework, can help providers evaluate a patient’s ability to stick to a treatment plan and help break down barriers when needed. They include:
- Social and Economic: Language barriers, low health literacy, unstable living conditions, and lack of insurance can be foundational barriers to following a treatment plan.
- Health Care System: Patient adherence is likelier to occur when there is a good patient/provider relationship and a seamless patient journey.
- Condition-Related: Lack of or very severe symptoms can inhibit a patient’s ability to follow a plan, as can mental health conditions like depression or psychosis.
- Therapy-Related: Duration, frequency, and complexity of treatment plan components as well as perceived side effects can play a role in inhibiting adherence.
- Patient-Related: If a patient lacks knowledge about their condition, has certain disabilities or impairments, or lacks motivation and confidence to execute the plan, they may have problems with adherence.
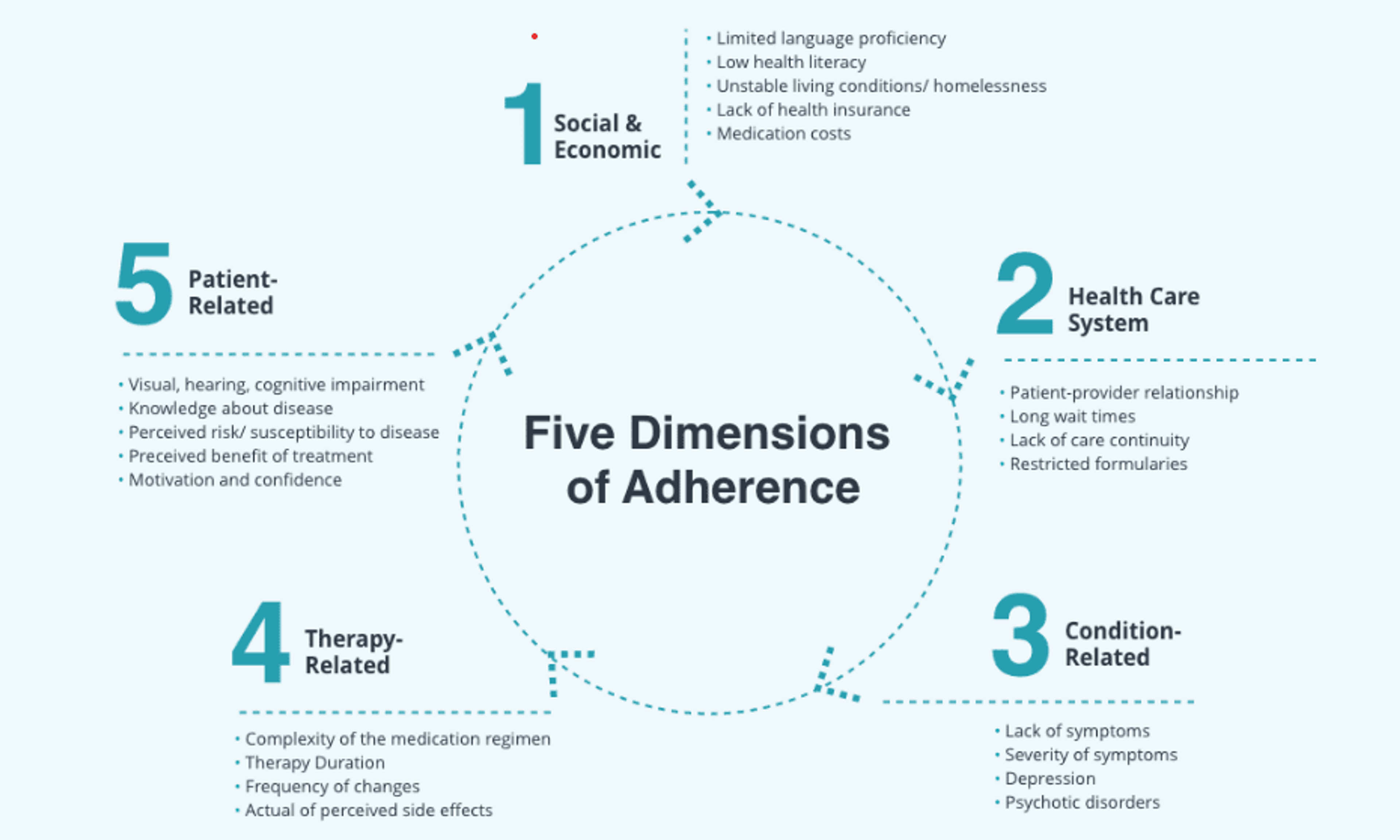
Image Source: pharmdlive.com
Patient adherence is important because it directly influences the effectiveness of medications and other therapies prescribed by a doctor to treat, manage, or cure conditions. When patient adherence is high, they are more likely to experience positive health outcomes, reduced disease progression, and improved overall well being.
On the contrary, non-adherence can lead to treatment failure, worsening of symptoms, and increased healthcare costs due to preventable complications.
Patient Preference
Patient preference encompasses an individual’s inclinations, choices, and priorities when it comes to medical treatments and interventions. Patient preferences are influenced by a variety of factors, including personal comfort, beliefs, values, lifestyle, and previous experiences.
Understanding patient preferences is essential for delivering patient-centered care. Healthcare providers who take patient preferences into account can offer treatments that align with patient comfort levels and goals. By recognizing and respecting patient choices, healthcare providers can foster a greater sense of empowerment and collaboration in the treatment decision-making process.
Patient preference plays a significant role in areas such as:
- Medication Choice: Patients may have preferences for certain types of medications based on factors like administration method, potential side effects, and dosing frequency.
- Treatment Modalities: Patients may prefer specific treatment approaches, such as surgery, physical therapy, or alternative therapies, based on their beliefs and comfort.
- Healthcare Settings: Patients might have preferences for where they receive care, such as hospitals, clinics, or home-based care.
- Shared Decision-Making: Patients are more engaged when they’re educated about treatment options and involved in decisions.
Patient preference is important because it contributes to higher adherence, which, as we already know, improves health outcomes.
5 Ways to Track Patient Adherence and Preference
Self-Reported Patient Diaries
Using patient diaries, patients can document their experiences on a daily basis, detailing when they adhere to treatment plans and any challenges they encounter in the process. They can also record their personal preferences along the way to build understanding for their provider.
While this method relies on patients’ memory and honesty, it’s one of the best ways to collect qualitative insights into their treatment journey.
Patient Surveys
Patient surveys are structured questionnaires that enable providers to gather both quantitative and qualitative data on patient adherence and preferences. These surveys can be designed to explore various aspects of treatment, from medication preference to communication channels to scheduling and more.
Crafting well-designed surveys ensures accurate data collection, shedding light on patient preferences and potential barriers to adherence.
Mobile Applications
Mobile applications designed for medication management and adherence tracking have gained popularity. These apps offer features such as medication reminders, dose tracking, and educational content delivery. Patients can actively engage with their treatment plans, and healthcare providers benefit from real-time adherence data, allowing for timely interventions.
Mobile apps are effective for tracking patient adherence in particular because they involve a process and device most individuals have already incorporated into their daily lives—using a mobile phone.
Research predicts that from now until at least 2030, mobile healthcare apps will grow at a compound growth rate (CAGR) of 11.6%Opens in a new tab, with tracking patient data one of their top use cases.
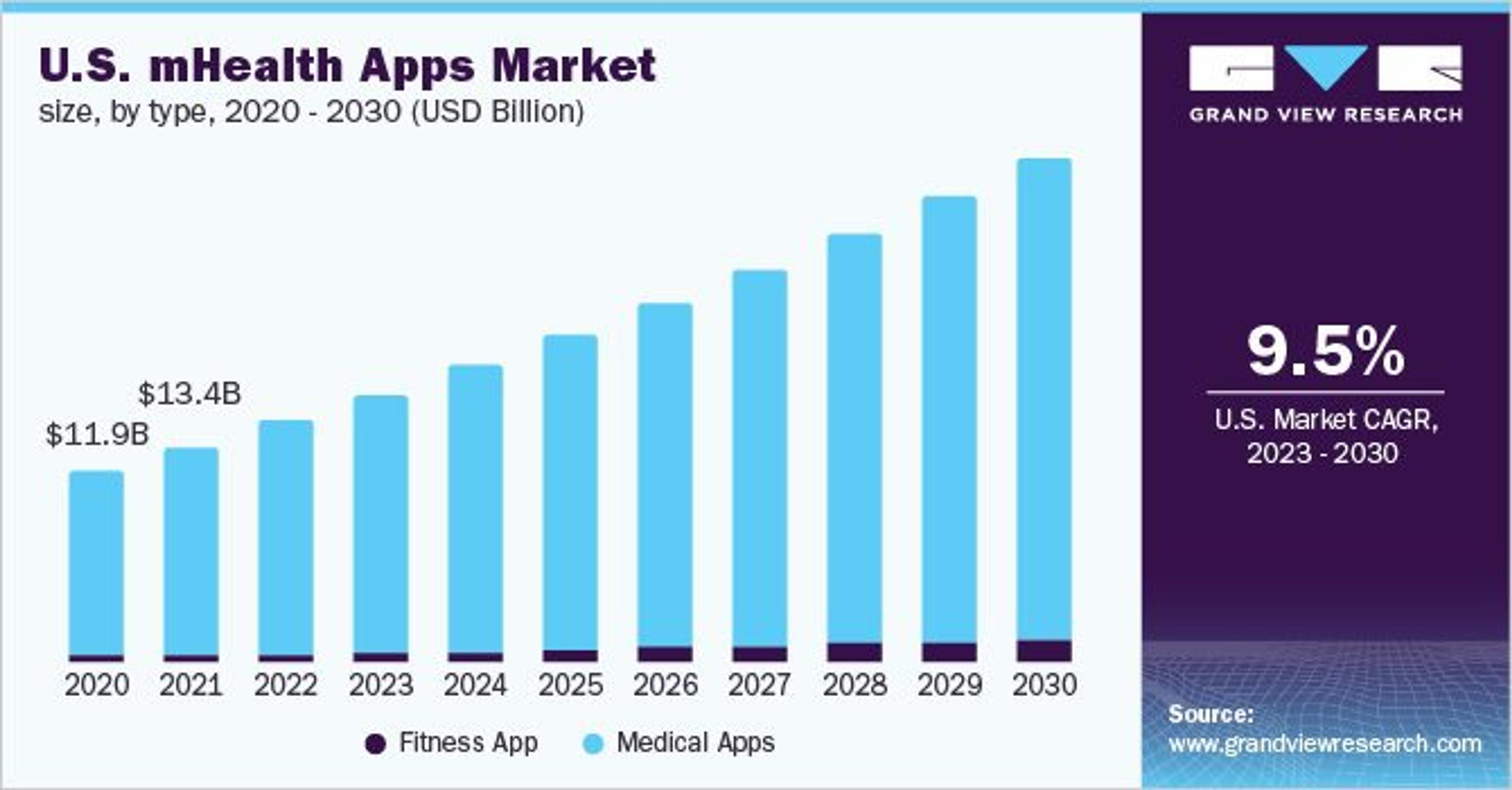
Image Source: grandviewresearch.com
Wearable Devices
Wearable devices such as smartwatches and fitness trackers have extended their functionality beyond fitness monitoring. When integrated with medication management apps, wearables can provide medication reminders and track medication intake. Like mobile apps, wearables seamlessly integrate into patients’ daily routines, contributing to consistent adherence monitoring.
Another powerful advantage of wearable devices for tracking patient adherence and preference is their automated nature. To use them, patients only have to wear the device, and the technology does the rest.
Centralized Electronic Health Records
Centralized Electronic Health Records (EHRs) serve as comprehensive repositories of patient health data. By incorporating patient adherence and preference data into EHRs, healthcare providers gain a holistic view of patients’ treatment experiences. This integration enables providers to identify important patterns, make informed decisions, and tailor treatment plans according to individual patient preferences.
Using MDM to Power Better Patient Adherence and Preference
Closely tracking patient adherence and preferences means your organization will be collecting, storing, and managing high volumes of data. To leverage the data to drive patient adherence, align with patient preferences, and drive better outcomes, it needs to be centralized and standardized effectively.
A healthcare master data management (MDM) solution is the key to achieving this. MDM delivers several benefits not possible with disparate data sources or traditional, manual data management methods.
These benefits include:
Integration and Accessibility
MDM integrates and standardizes data from various sources, including the ones we mentioned in the previous section, like mobile apps, wearable devices, surveys, and EHRs. It provides a centrally-accessible single source of data truth so that providers and support professionals can work together to provide optimal patient care.
Personalized Treatment Plans
MDM platforms help healthcare providers know their patients better via accessible patient data, and personalize experiences to align with their preferences and needs. Doing so provides better support to individual patients so they are able to adhere to treatment plans more successfully.
Real-Time Monitoring and Intervention
With MDM, healthcare organizations can implement real-time monitoring of patient adherence. Data can be integrated from various sources into the MDM system in real time, providing up-to-date information on medication intake and treatment adherence. When deviations from the treatment plan occur, providers can intervene promptly, ensuring patients receive the support they need.
Predictive Analytics
MDM’s analytical capabilities enable the identification of patterns and trends in patient adherence behaviors. By leveraging predictive analytics, healthcare providers can anticipate potential adherence challenges and design proactive interventions. This predictive approach helps prevent non-adherence and reduces the risk of treatment disruptions.
Communication and Engagement
MDM supports improved patient engagement and communication. Providers can use the consolidated patient data to initiate meaningful conversations about treatment preferences, challenges, and potential modifications, better engaging patients throughout their treatment plans and involving them in shared decision-making to foster a sense of ownership.
Continuity of Care
MDM ensures continuity of care by providing a comprehensive overview of patient history and adherence across different care settings. This seamless transition of information between healthcare providers promotes consistent care delivery, reducing the likelihood of disruptions in treatment adherence during transitions.
Uplevel Your Patient Adherence Tracking with Gaine
Gaine’s Coperor platform is an MDM tool designed uniquely for healthcare and the life sciences. Using Coperer, you can establish a single, accessible source of patient data truth to help you track adherence more effectively and support your patients in achieving better health outcomes.
To learn more, view this demo of Coperor today.