blog
The Complete Guide to Remote Patient Monitoring
SECTIONS
Remote patient monitoring (RPM) is a fairly new and transformative approach to patient care, leveraging digital technologies to monitor patients outside of conventional clinical settings. RPM method enables continuous care and real-time health monitoring without needing patients to be physically present at a healthcare facility.
The significance of RPM has surged in recent years as digital adoption among the general population has increased, and modern technology has advanced to the point where remote patient monitoring can be done consistently and reliably. When executed well by providers and patients, RPM can enhance patient outcomes, reduce healthcare costs, and improve access to care (among other benefits).
This guide delves into the comprehensive landscape of remote patient monitoring in 2024, including its benefits, challenges, and the pivotal role it’s playing in the evolution of healthcare delivery.
Key Takeaways:
- Remote patient monitoring enables continuous and real-time health monitoring, enhancing patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs.
- The evolution of RPM is propelled by technological advancements, including the integration of AI and wearable health devices.
- RPM benefits include improved patient access to care, operational efficiencies for healthcare providers, and scalable solutions for healthcare systems.
- Successful RPM implementation involves strategic planning, technology selection, and seamless integration with existing healthcare systems.
What Is Remote Patient Monitoring?
Remote patient monitoring is an innovative healthcare delivery method that utilizes digital technologies to track and transmit patients’ medical and health-related data from a distance to healthcare providers for assessment and recommendations. This technology enables the monitoring of various health metrics, such as blood pressure, heart rate, glucose levels, and oxygen saturation, among others.
RPM facilitates a continuous connection between patients and their care teams, which allows for timely interventions, personalized care plans, and improved management of chronic conditions.
The evolution of RPM in healthcare has been marked by significant advancements in technology and a growing emphasis on patient-centered care. Initially, RPM was utilized primarily for monitoring chronic conditions and post-discharge patients to reduce readmission rates.
Over time, its application has expanded dramatically, driven by technology innovations, the integration of artificial intelligence, and the increasing adoption of wearable health devices. The impact has been significant for patients and providers alike—94% of providersOpens in a new tab say that implementing RPM has improved patient outcomes, and 73% say their organizations are yielding a return on investment.
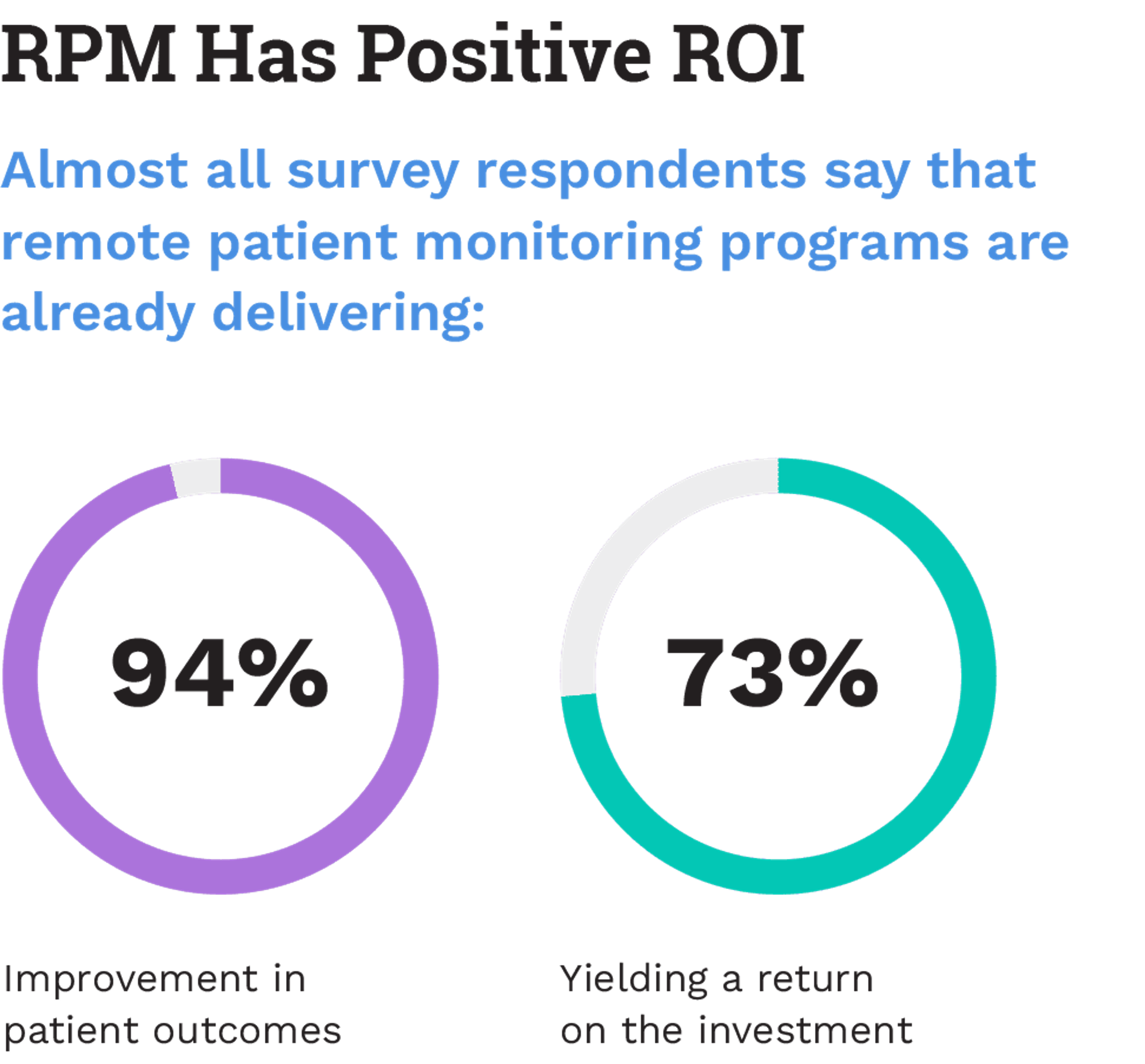
Image Source
RPM is also a critical component of the broader telehealth landscape, which encompasses a range of services including virtual consultations, e-prescriptions, and health education. While telehealth refers to the entirety of remote and technology-driven healthcare services, RPM specifically focuses on the continuous, real-time monitoring of patient health data.
Together, they represent a shift towards more accessible, cost-effective, and patient-centered healthcare models, bridging the gap between patients and providers, regardless of physical distance.
Benefits of Remote Patient Monitoring
Remote patient monitoring offers a myriad of benefits that extend across the spectrum of care delivery. By connecting patients and providers through technology, RPM enhances the quality, accessibility, and efficiency of healthcare services. This section will explore the multifaceted advances of remote patient monitoring for patients, healthcare providers, and healthcare systems at large.
For Patients
Remote patient monitoring significantly improves patient access to care, particularly for those in remote areas or with mobility challenges. By enabling healthcare monitoring remotely, patients can avoid the inconvenience and expense of frequent hospital visits.
This level of accessibility fosters more than 40%Opens in a new tab higher patient adherence and engagement as individuals become active participants in their health management.
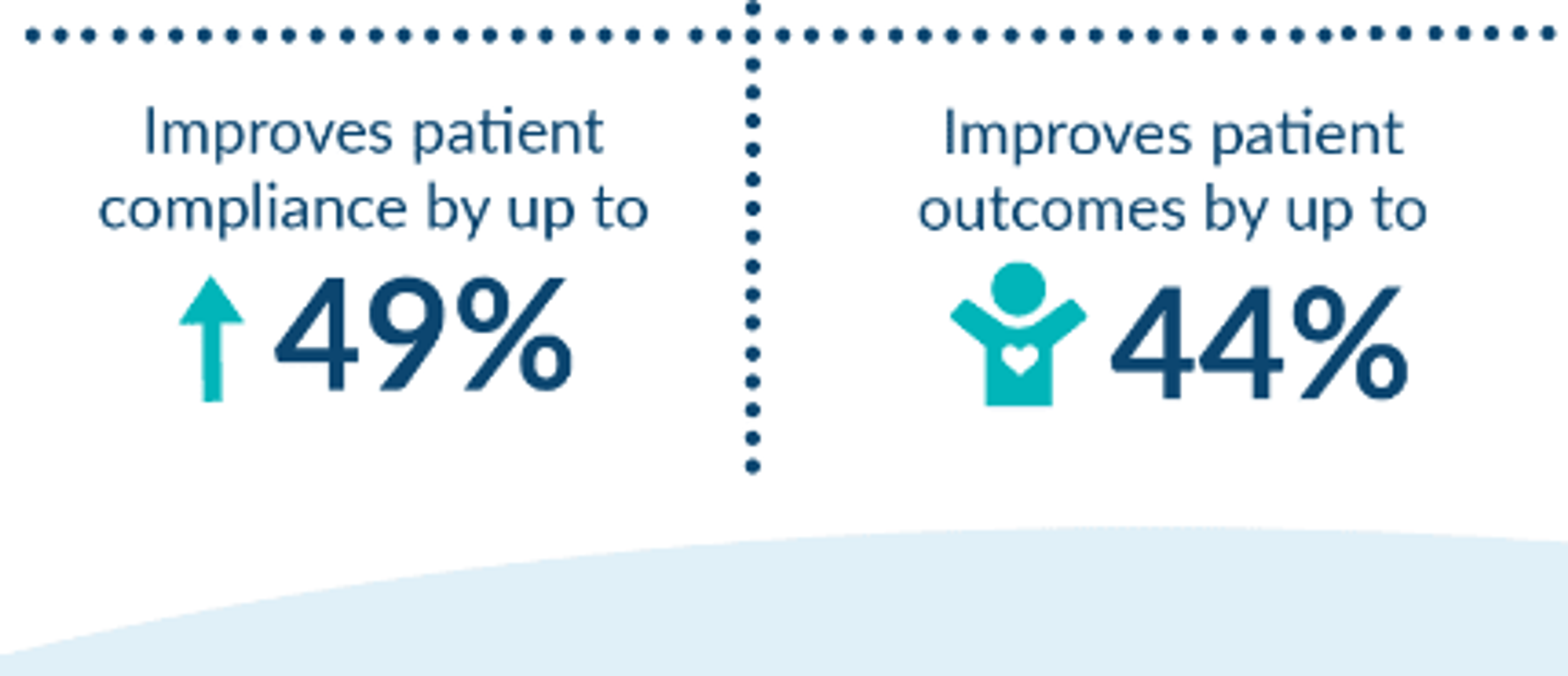
Image Source
With real-time data sharing, patients can receive immediate feedback and adjustments to their care plans, leading to better health outcomes. Chronic conditions are managed more effectively, and the early detection of potential health issues reduces the need for emergency interventions.
For Healthcare Providers
Healthcare providers benefit from the operational efficiencies created by RPM. By automating routine monitoring tasks, providers can allocate their time and resources more effectively, focusing on cases that require direct intervention.
This efficiency contributes to reduced healthcare costs, as remote patient monitoring can help prevent hospital readmissions and unnecessary emergency room visits. Moreover, RPM facilitates improved patient management through the continuous flow of data, enabling providers to make more informed decisions and tailor treatments to individual patient needs.
For Healthcare Systems
At the systemic level, RPM offers scalability, allowing healthcare services to reach a broader population without the need for proportional increases in resources or facilities. Data collected through remote patient monitoring systems provides valuable insights into population health trends, disease patterns, and treatment outcomes, driving evidence-based improvements in care delivery.
Furthermore, RPM can enhance care coordination among different healthcare providers, ensuring that patient care is seamless, integrated, and efficient across the healthcare continuum.
Implementing Remote Patient Monitoring
Successfully implementing Remote patient monitoring (RPM) requires careful planning and execution. Here’s a concise guide on the right steps to prioritize:
- Assessment and Planning: Identify patient needs and goals of the RPM program. Consider the specific conditions to monitor and the expected outcomes.
- Technology Selection: Choose RPM devices and software that integrate seamlessly with existing healthcare systems. Ensure the technology is user-friendly for both patients and providers.
- Vendor Selection: Select a vendor based on their reliability, support services, technology compatibility, and scalability. It’s crucial that the RPM solution can grow with your healthcare practice and adapt to evolving needs.
- Integration and Training: Integrate the RPM system with existing electronic health records (EHR) for smooth data flow and access. Provide comprehensive training for staff and patients to ensure effective use of the technology.
By focusing on these key areas, your healthcare organization can set up an RPM program that enhances patient care and improves operational efficiency within a concise, manageable framework.
Manage RPM Data Confidently with Gaine Solutions
As healthcare organizations embrace remote patient monitoring on a greater scale, managing the influx of patient data securely and efficiently becomes paramount. Gaine is at the forefront of this challenge, offering advanced data management capabilities that ensure the seamless integration and interpretation of RPM and other healthcare data.
Discover how Gaine Solutions can transform your RPM data management.