blog
The Handbook of Data Privacy in Healthcare
SECTIONS
Data privacy gives control to the patient, so they can choose where and how businesses collect and use their information. The most important part of keeping a patient’s information private is ensuring no unlawful or unauthorized people access the data.
Explore the challenges with data privacy and the steps you can take to improve your healthcare organization’s privacy standards.
Key Takeaways:
- Medical data is the most valuable data on the black market. However, healthcare organizations have some of the smallest security budgets.
- Reduce data breaches and unauthorized use by storing data on a centralized system you can track and monitor.
- Regular training and action plans are proactive measures you can take to reduce the impact of data breaches.
Challenges in Healthcare Data Privacy
Healthcare data breachesOpens in a new tab are on the rise. COVID-19 triggered a significant jump in data breaches as more healthcare organizations moved to remote work, which made their data more susceptible to breaches. Companies that didn’t have systems in place before COVID were especially vulnerable as cyber hackers took advantage of the confusion to perform illegal activities.
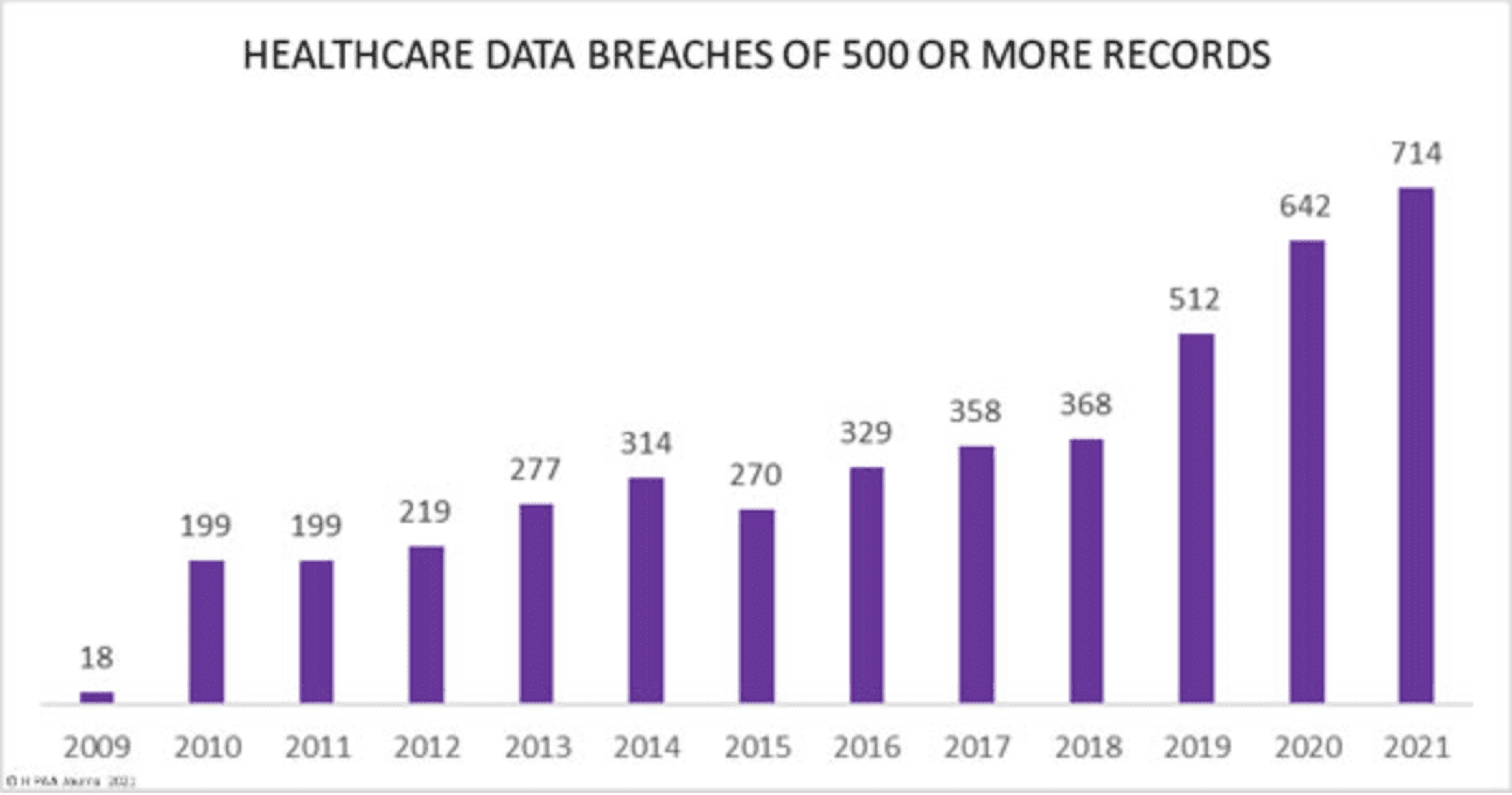
Image Source: HIPPA Journal
Today, life sciences and biotech organizations have found ways to protect and securely distribute data while minimizing its exposure to unauthorized users to protect users’ privacy. However, there are still some challenges that healthcare organizations continue to face.
Use of Electronic Health Records
Electronic health records provide a valuable way for those in life science and biotech to track patients and their habits. In addition, they can access crucial information on their care from physicians and other health providers.
Today, 75% and 97% of healthcare providers use electronic health recordsOpens in a new tab. The largest segment using electronic health records is general care and children’s care. Meanwhile, specialty services have the lowest percentage of providers using the service.
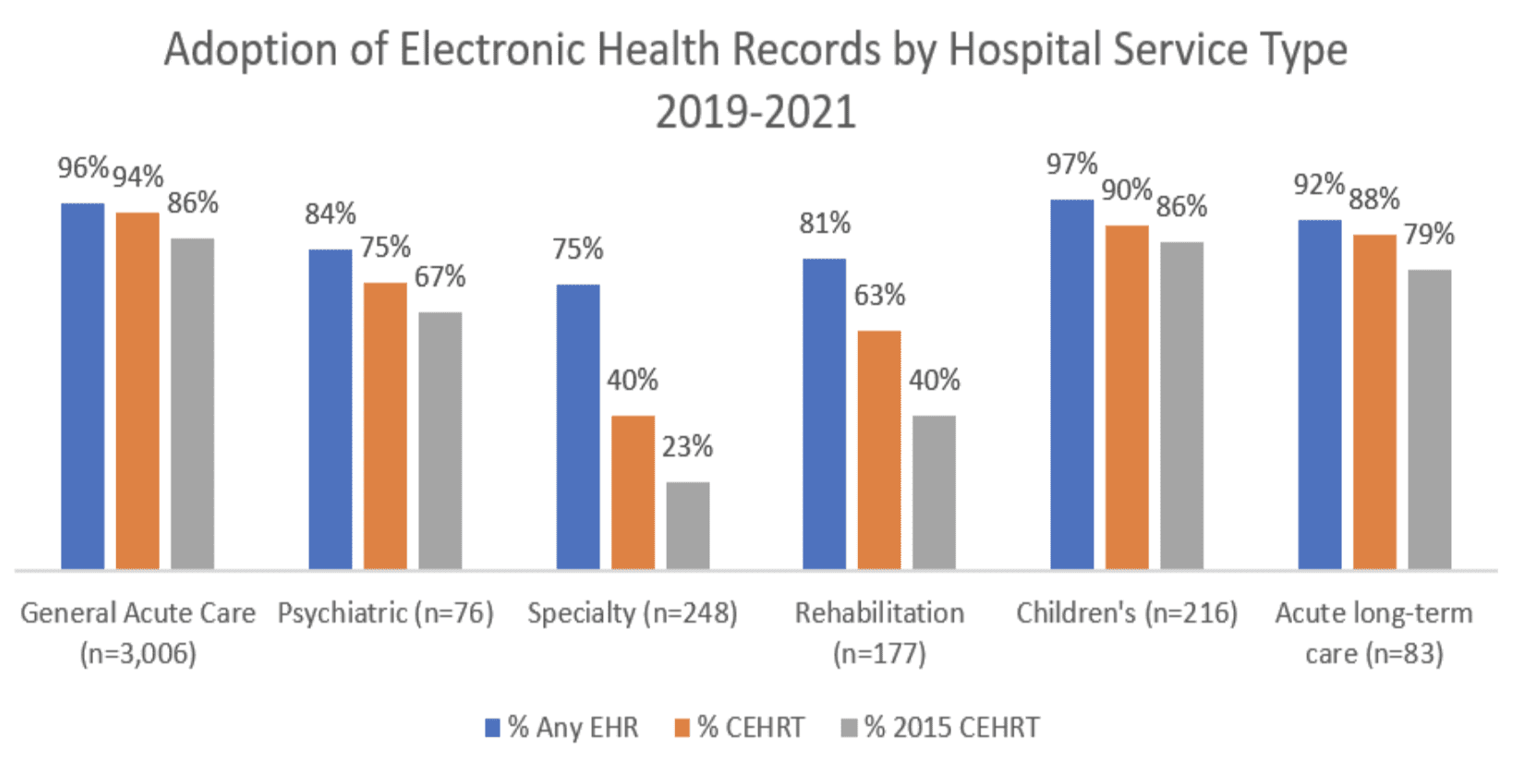
Image Source: HealthIT.gov
There is also a downside to electronic health records. Keeping all that data online for everyone involved in a patient’s care to view makes that record vulnerable to a data breach or data misuse if proper precautions aren’t in place to limit who can access that information.
More Access Granted
Because health records are moving online, providers can share that information with more people involved in the patient’s care or for healthcare marketingOpens in a new tab. As a result of the increased health data exchange, a patient can have multiple people accessing parts of their data, including several physicians and scientists working on clinical trials they’re involved with. For example, asking for a second or third opinion is very common, which adds new providers to the list of authorized people accessing that patient’s online data.
In addition to people, more devices have access to electronic health records. For example, about 20% of the US population wears a smart wearable monitorOpens in a new tab. Some examples include:
- ECG monitors
- Blood pressure monitors
- Biosensors
- Fitness trackers
While these devices give biotech scientists and engineers more insights into their patients, they also pose additional risks for data breaches if they aren’t appropriately secured.
Small Security Budgets
About five percent of healthcare IT budgetsOpens in a new tab go to cybersecurity. In contrast, 15% of budgets in other industries go towards cybersecurity.
However, medical records are the most valuable form of dataOpens in a new tab. On the black market, healthcare data records can cost up to $250 per record, compared to $5.40 for payment card data, the second most valuable data.
Healthcare companies should increase their security budget to reflect the value of the data they protect.
6 Tips to Improve Data Privacy in Healthcare
These six tips will help you overcome those data privacy challenges and threats to build a more secure healthcare management system for your patients.
1. Conduct Regular Training
Roughly 91% of healthcare administrators said data securityOpens in a new tab is a top priority, yet 62% of employees didn’t feel adequately prepared to address cyber risks.
Ensure all your biotech scientists and engineers understand the proper protocol for accessing, sharing, and securing information to protect the privacy of your patients. Fraud Watch recommends holding cybersecurity trainingOpens in a new tab every four to six months. These trainings will serve as refresher courses on data governance in healthcare.
2. Use a Master Data Management System
A master data management system creates a single source of truth. It reduces the number of mistakes from sharing data and helps you track who accesses patient records. In addition, by keeping all patient records in one place, you have more control over the data and ensure it’s compliant with current regulations and privacy policies.
3. Keep Your Systems Updated
Outdated systems make your data more susceptible to cyberattacks and data breaches. Updating your software and using new technology like computers increases your data protection.
Any devices or systems connected through the internet are susceptible to data breaches, including wearable devices used by people in your trials. Your company should focus on updating these devices and the larger software and technology.
4. Control Mobile Access
Over 83% of the world’s population owns a smartphoneOpens in a new tab. While mobile devices like smartphones and tablets make recording and accessing healthcare information convenient, they also pose a threat. You can reduce this threat by restricting the use of mobile devices for downloading healthcare information, including limiting what information your patients can access on their mobile apps.
In addition, you can protect the information available on mobile devices by encrypting it for an extra layer of security and privacy.
5. Regularly Perform Risk Management
During your routine risk management, also look over your security systems. How you save and secure information is just as important as the studies you perform, as it can significantly impact a patient’s health and safety.
Risk management identifies potential data risks, assesses the risk, and controls the threat through new procedures or software.
6. Have Plans in Place
Cyberattacks caused an average shutdown of ten hours and cost $45,700 per hour for midsize hospitals. During COVID, some healthcare organizations had to deny new patients, close their doors, and even turn off their power to keep out cyberattacks.
These are extreme reactions and are preventable with plans in place. Proactively planning for cyberattacks or data breaches gives your employees an action plan they can use when a data breach or privacy infraction occurs. This helps you identify privacy breaches faster and address them sooner to reduce the impact on your patients and your organization.
Improve Your Healthcare Data Management
Your healthcare data privacy system starts with limiting the amount of access to medical data. Our provider data management systems centralize your data so you can track, manage, and secure each patient’s information to reduce data breaches and increase your data privacy.
Contact us to learn more about our data management systems for healthcare.