blog
The Ins and Outs of a Remote Patient Monitoring System
SECTIONS
Today’s healthcare landscape is defined by rapid digital transformation and emerging technology-driven norms such as telehealth, data-informed decision making, and new tools like remote patient monitoring systems. The latter of these has proven particularly impactful in improving patient outcomes long-term.
With remote patient monitoring in place, providers can stay connected to their patients even when they leave clinical settings. They can view critical health data (ex: vitals) in real-time, ensure patient recovery and/or adherence is happening smoothly, and quickly intervene when problems arise. As a result, they’re able to reduce costly readmissions and recurrence of health issues, and optimize the patient journey.
In this guide, we’ll explore how remote patient monitoring systems work, key features and use cases, and ways healthcare organizations can successfully implement to enhance quality and efficacy of care.
Key Takeaways:
- Remote patient monitoring systems are powered by wearable devices that often work in tandem with medical devices and software interfaces.
- Benefits include improved patient access, higher patient engagement, better data management, and increased efficacy of care.
- To keys to effective remote patient monitoring are employee and patient training, and integration with existing systems.
What is a Remote Patient Monitoring System?
A remote patient monitoring system (RPMS) is an advanced healthcare solution designed to monitor patients’ health data outside traditional clinical settings. This technology is pivotal for continuous health monitoring, especially for patients with chronic conditions, post-operative care needs, or elderly individuals requiring consistent observation.
Key components of a remote patient monitoring system include:
- Wearable Sensors/Devices: These collect health metrics such as heart rate, glucose levels, blood pressure, and sleep patterns. Examples include smartwatches, fitness trackers, and specialized medical wearables.
- Medical Devices: Specifically designed for patient monitoring, these include devices like ECG and blood glucose monitors that patients can use at home.
- Data Processing Unit: Central to the system, this unit receives, stores, and analyzes the data collected from sensors and devices. It’s typically a cloud-based platform that securely processes patient data.
- Patient Interface: Usually a smartphone app or online portal where patients can view their data, receive health alerts, and sometimes communicate with healthcare providers.
Remote patient monitoring systems can collect and transmit data in real-time so that it can be analyzed by healthcare professionals as needed. Providers use this data to monitor patterns, adjust treatment plans, and intervene when necessary. This new level of connection between patients and providers helps drive stronger patient adherence and better overall outcomes.
Use of Remote Patient Monitoring Systems on the Rise
Like most components of telehealth, the market for remote patient monitoring systems and the number of patients using them saw a significant jump during and immediately after the pandemic.
Over the next several years this growth is projected to continue, with the number of RPMS users surpassing 70 millionOpens in a new tab by 2025, and the market itself growing more than doubling in size between 2023 and 2030.
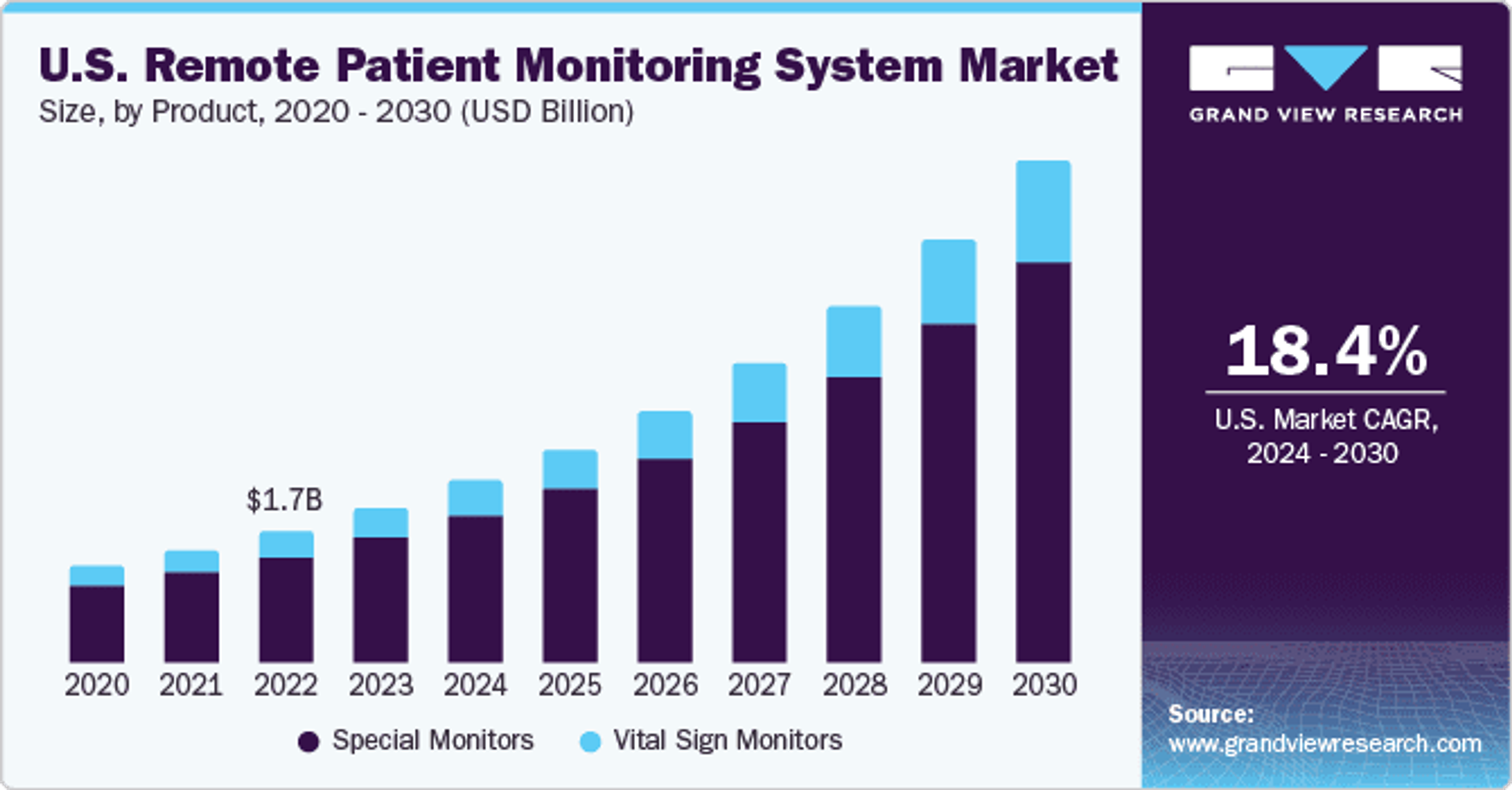
Image Source
For healthcare providers, this means making remote patient monitoring systems a regular part of their treatment planning—and adopting the tools, technologies, and processes required to use it—are quickly becoming a baseline standard for modern care.
Benefits of RPMS
There’s no double that remote patient monitoring systems are enhancing the quality of care providers are able to deliver to patients in a variety of settings. With ongoing access to health data, physicians and other care providers can make informed decisions while quickly recognizing issues that arise.
The most important RPMS benefits include:
Improved Patient Access to Care
RPMS eliminates geographical barriers, offering patients in even the most remote areas easy access to continuous healthcare. This is particularly vital for those with chronic conditions or mobility issues, as it reduces the need for frequent hospital visits.
Enhanced Patient Engagement and Empowerment
With real-time data at their fingertips, patients become more involved in their health management. This empowerment encourages better adherence to treatment plans and fosters a stronger understanding of their health conditions, leading to improved health outcomes.
Further, remote patient monitoring systems align with habits people are already incorporating into their regular lives. Today, 6 in 10 consumer householdsOpens in a new tab already have wearables, and 87% say they use them to track health data. This is a positive indicator for successful patient adoption of RPMS technology.
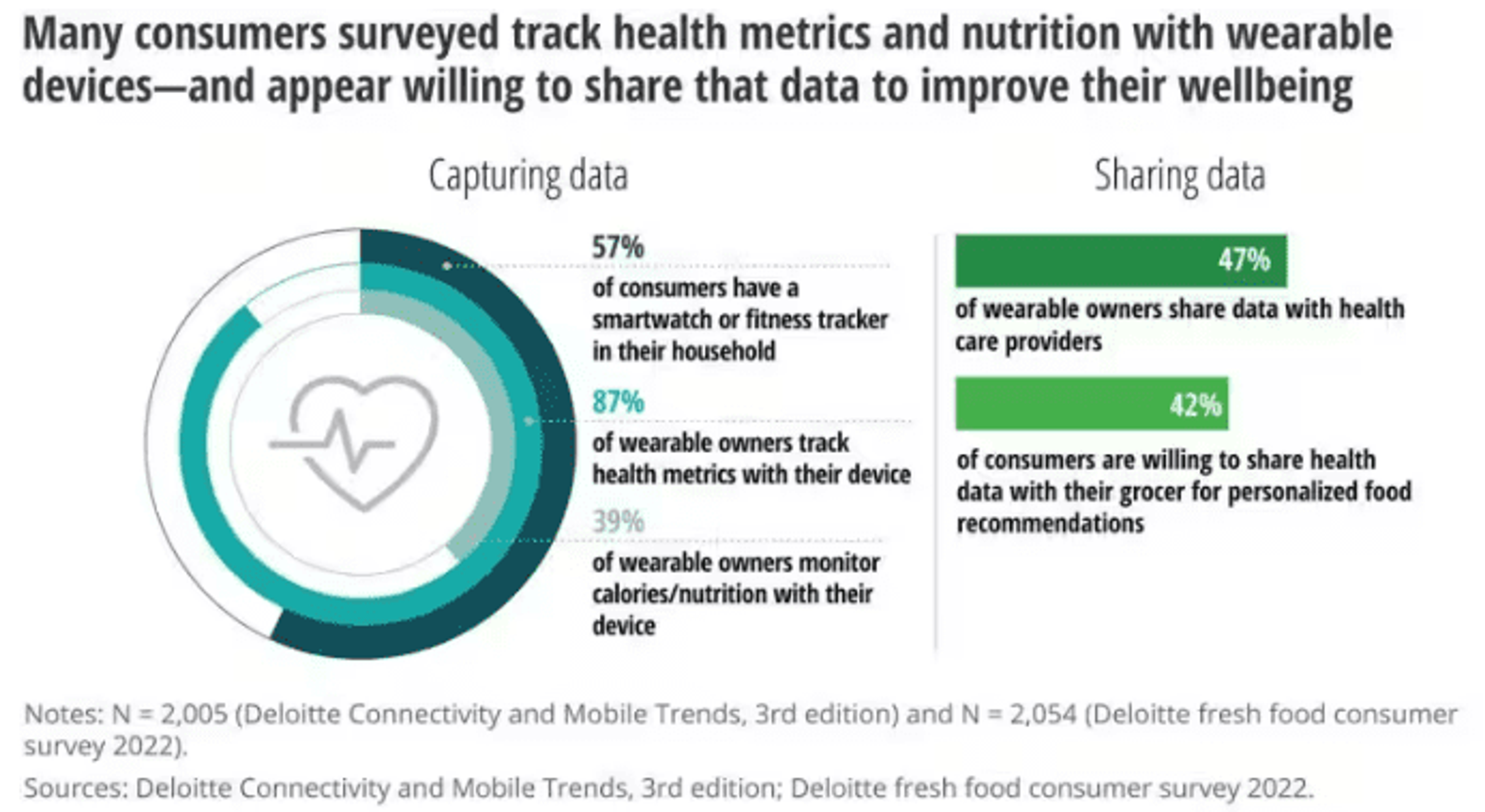
Image Source
Efficient Patient Data Management for Healthcare Providers
RPMS streamlines the collection and analysis of patient data, providing healthcare professionals with accurate, up-to-date information. This efficiency allows for timely interventions, personalized care plans, and better management of patient health, reducing the incidence of emergency visits and hospital readmissions.
Increased Efficacy of Care
By continuously monitoring patient health, remote patient monitoring systems aid in the early detection of potential health issues. This proactive approach not only improves patient outcomes but also reduces the burden on healthcare facilities, leading to less readmissions and more efficient resource utilization.
Implementing a Remote Patient Monitoring System
Effectively implementing a remote patient monitoring system involves several steps, each contributing to the system’s overall success as well as provider and patient capabilities to use it:
1. Choose the Right Technology
When it comes to remote patient monitoring, not all systems are created equal for every use case. It’s up to the provider organization to evaluate devices and software—including functionality, reliability, and compatibility with existing systems—and then choose the one best suited for their situation. Ease of use for patients, data accuracy, and security should all be considered paramount in this decision.
2. Training Staff and Patients
RPMS is only as impactful as the extent to which patients and staff can actually use it. It’s important to train employees effectively on how a new remote patient monitoring system works and when they should be using it.
Equally important is educating patients on how to use the devices, and on the importance of regular data transmission, which is key to patient compliance and the success of the program.
3. Ensure Regulatory Compliance
The RPMS must comply with healthcare regulations such as HIPAA in the U.S. This includes safeguarding patient data privacy and ensuring secure data transmission. Vendors in the healthcare space should have a strong understanding of these regulations and be able to speak extensively about how their systems stay compliant.
4. Integrating with Existing Systems
Remote patient monitoring systems should be seamlessly integrated with existing healthcare systems for efficient data management, and to avoid data silos or duplication of efforts. When selecting an RPMS, be sure to discuss interoperability with the vendor and confirm its capabilities related to your current tools.
5. Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation
Implementing an RPMS is not a one-time event but an ongoing process. Continuous monitoring of the system’s performance, regular feedback from staff and patients, and making necessary adjustments are essential for long-term success.
By following these steps, your healthcare organization can implement a robust RPMS that not only enhances patient care but also aligns with regulatory standards and operational best practices, leading to enhanced care delivery and improved health outcomes.
RPMS in Your Larger Data Strategy
There’s no doubt that remote patient monitoring has transformative potential for enhancing long-term care quality and making patients active participants in achieving better health outcomes.
At the same time, it can become a complex new factor in an organization’s larger data strategy. To avoid challenges that slow down the efficacy of new RPMS technology, it’s essential to plan thoroughly not only for system integration, but also for alignment with larger data management strategies.
Gaine’s Coperer platform is helping healthcare and life sciences organizations create an ecosystem-wide single source of data truth that streamlines data from various sources while delivering optimum visibility, accessibility, and security.
Learn more here or start your real-time Coperer demo today.