blog
Top Healthcare Trends to Watch in 2023
SECTIONS
Innovation in healthcare and the life sciences has accelerated at remarkable speeds over the last few years. Even during COVID-19 restrictions in 2020, when the U.S. economy experienced a brief recession and the workforce contracted, the life sciences industry still exhibited growth. As uncertainty continues to loom over the global economy, investors and business leaders have a keen eye on life sciences trends for 2023.
This guide explores emerging trends that will likely characterize growth and development in the life sciences, healthcare, and pharmaceutical industries in the coming year.
Key Takeaways:
- New technology and changing consumer demand are behind emerging trends in the life sciences sector.
- Life sciences organizations are changing how they orchestrate clinical trials and manage patient consent.
- Connected health monitoring devices and next-generation cell and gene therapies are two major investment opportunities for life sciences companies in 2023.
2023 Life Sciences Trends
Developments in technology and evolving patient needs and consumer demand are driving several broad trends in the life sciences industry. Here are four to watch in 2023.
1. Patient-Centricity
In recent years, the pharmaceutical industry has largely transitioned from a disease-centered approach to clinical trials to patient-centric prioritiesOpens in a new tab that recognize patients as critical stakeholders in the advancement of new medications and treatments. In practice, this shift means researchers design clinical trials and research methods with a focus on patient well-being and view patient perspectives and experiences as a primary dataset.
StudiesOpens in a new tab of patient participation and engagement in clinical trials during the last decade indicate that traditional disease-centered approaches often cause overwhelmingly negative patient experiences and fail to produce useful results:

Image Source: Accenture
- Low patient enrollment prevents 85% of trials from starting on time.
- Poor experiences with staff and care providers cause 30% of patients to drop out of clinical trials.
- Trials terminate early 19% of the time due to falling patient enrollment, costing life science organizations $800 billion in lost value.
Alternatively, designing trials specifically for the quality of patient experience drives engagement, resulting in higher success rates for trials and more robust data published in the literature. Developments in technology, such as online forums for trial patients, remote support groups, and better access to medical information are helping life science organizations implement patient-centric approaches. As a result, pharmaceutical companies have begun incorporating more patient feedback into published studies and guidelines.
2. Privacy and Consent Management in Omnichannel Marketing
The development of patient-centric approaches to life science processes increases the need for life science organizations to contact and market directly to care providers and patients. However, a growing body of privacy regulations, such as the European Union’s General Data Privacy Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), restrict the use of mainstream marketing tactics by healthcare and life science organizations.
Life science organizations maintain compliance with data privacy regulations by adopting a distinction in consent management between patients’ consent for the storage of their personal data and data consent for marketing activities.
- Processing consent: This applies to patient data stored in IT systems such as web portals and customer relationship managementOpens in a new tab (CRM) platforms. Encryption for data in transit and at rest combined with front-end multifactor authentication satisfies the requirements of regulations like the GDPR and CCPA and validates patient consent for the use of these systems.
- Marketing authorization or consent: Healthcare and life science organizations that contact care providers and patients for marketing purposes can demonstrate consent through either soft opt-in or explicit consent forms. Soft opt-ins refer to the use of prior contact as implicit consent. As life science organizations take a more omnichannel approach to marketing through email and social media, more organizations are replacing soft opt-ins with explicit consent requests for all digital contact.
3. Growth in Health Monitoring Devices
Developments in wearables, IoT, and AI-based technologies have attracted a growing number of tech companies without specific medical expertise or credentials to the consumer-grade health device market. As these companies expand biotech access to cutting-edge IT, the medical device market continues to experience more demand.
In the last eight years, the percentage of surveyed healthcare consumers using health monitoring devices or consumer-grade fitness trackers has doubled from 24% in 2015 to 49% in 2022Opens in a new tab. Commonly monitored health metrics and conditions include blood sugar, blood pressure, respiratory function, and mood. Vendors of health monitoring devices may sell them as dedicated devices or as apps and features on smart devices such as phones and watches.
Beyond market growth from increasing consumer demand, the rise of health monitoring devices benefits care providers as well. With access to continuous patient data and baseline conditions, care providers can develop a more holistic understanding of patient health and more individually focused feedback and recommendations.
4. Next Generation Cell and Gene Therapy (CGT) and Investigational New Drugs (INDs)
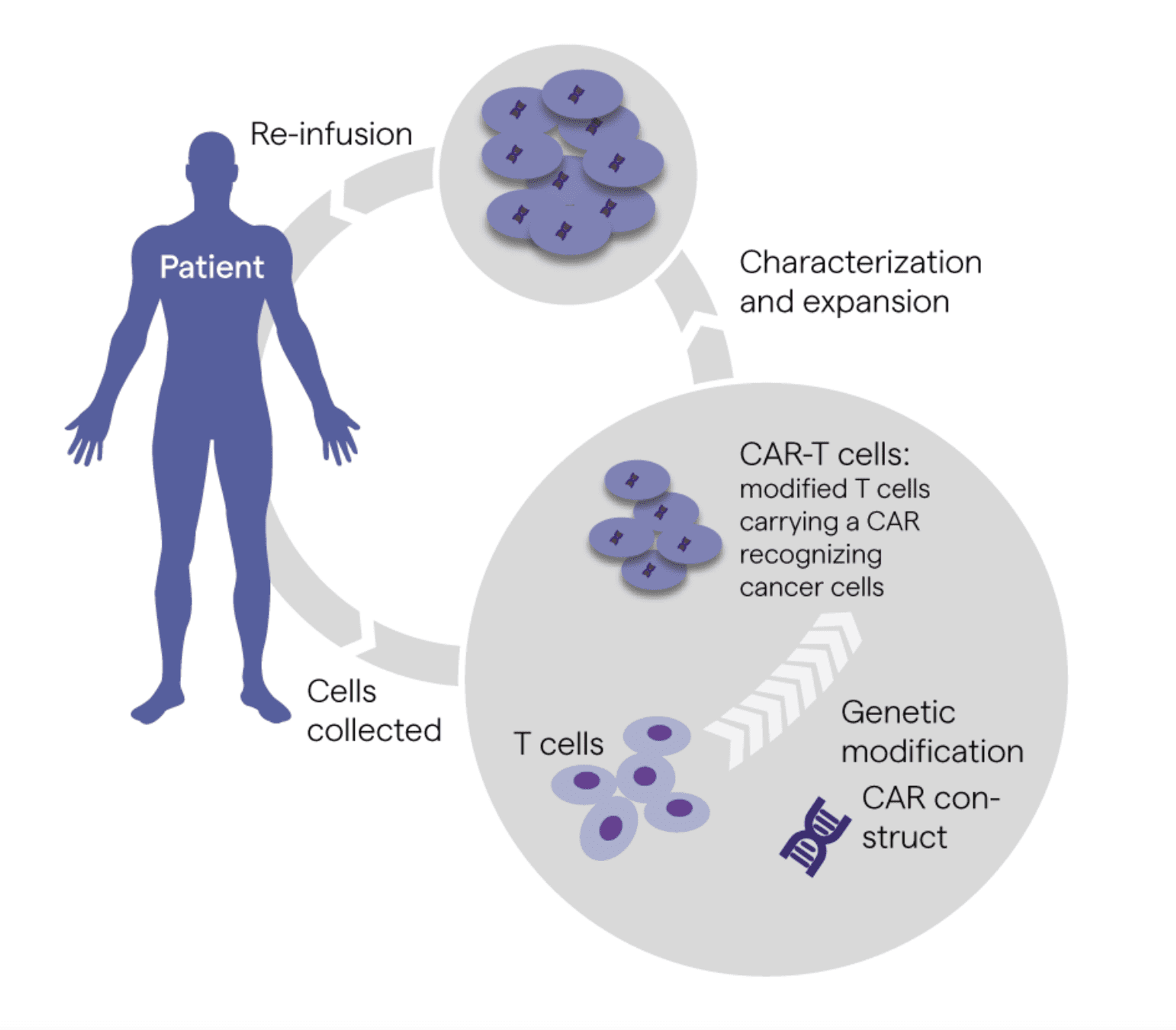
Image Source: Lonza Bioscience
In 2022, the U.S. Food & Drug Administration (FDA) received more than 3000Opens in a new tab clinical trial applications for cell and gene therapies (CGTs) and investigational new drugs (INDs). Among surveyed biopharmaceutical executives, 95% identify CGTs and INDs as integral to their 2023 strategies.
As the FDA approved fewer than 100Opens in a new tab such applications in the last five years, the expected approval of dozens to hundreds in the next year signals a major shift in life sciences R&D spending. The cost of CGTs and INDs is high – even compared to last-line oncology drugs and immunosuppressant biologics – with a handful of approved therapies currently priced at $2-3 million.
FDA approval and market availability of costly new treatments will challenge existing employer health benefit practices and may invite a new tier of federal regulations for classifying medical treatments under insurance policies. Nevertheless, the willingness of many pharmaceutical and life sciences companies to shoulder the cost of R&D up front suggests that many major players expect a viable solution to arise.
Master Data Management for Healthcare and Life Sciences with Coperor
Data management in healthcare and life sciences requires expertise in the industries’ unique challenges. Coperor by Gaine is an industry-first master data management platform designed for healthcare and life science applications.
To learn more, contact Gaine today.