blog
The Handbook of Regulatory Compliance in Healthcare
SECTIONS
Navigating the complex landscape of healthcare regulatory compliance is crucial for ensuring safe, effective, and high-quality healthcare services. Today, achieving strong compliance requires a wide range of knowledge, adaptability, and technology as well as an informed and intentional approach.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore essential aspects of regulatory compliance in healthcare, common challenges, and the steps your organization can take to build a strategy that keeps your data, resources, employees, and patients safe at every turn.
Key Takeaways:
- Compliance is the top risk area covered by healthcare audit services.
- Important healthcare compliance regulations include HIPAA, The Affordable Care Act, and the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act (HITECH).
- Key regulatory bodies include the Department of Health and Human Services, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, and the Food and Drug Administration.
- Modern healthcare compliance agencies require the support of software tools to manage data and operate at the necessary speed and scale.
- Important aspects of a strong healthcare compliance strategy include employee training, regular risk assessments and audits, adoption of the right technologies, and strong data management.
Understanding Healthcare Regulatory Compliance
By definition, healthcare regulatory compliance means adhering to laws, regulations, guidelines, and specifications relevant to healthcare practices and providers. It encompasses a wide range of areas including patient care, data privacy, billing practices, and the use of medical technology (among others).
The primary goal of regulatory compliance in healthcare is to ensure that organizations provide safe, effective, and high-quality healthcare services while protecting patient information and rights. It’s about more than just following laws, but creating a culture of accountability and integrity within healthcare organizations.
Compliance is by far the top risk areaOpens in a new tab covered by healthcare organization audits, demonstrating the level of priority it currently demands.
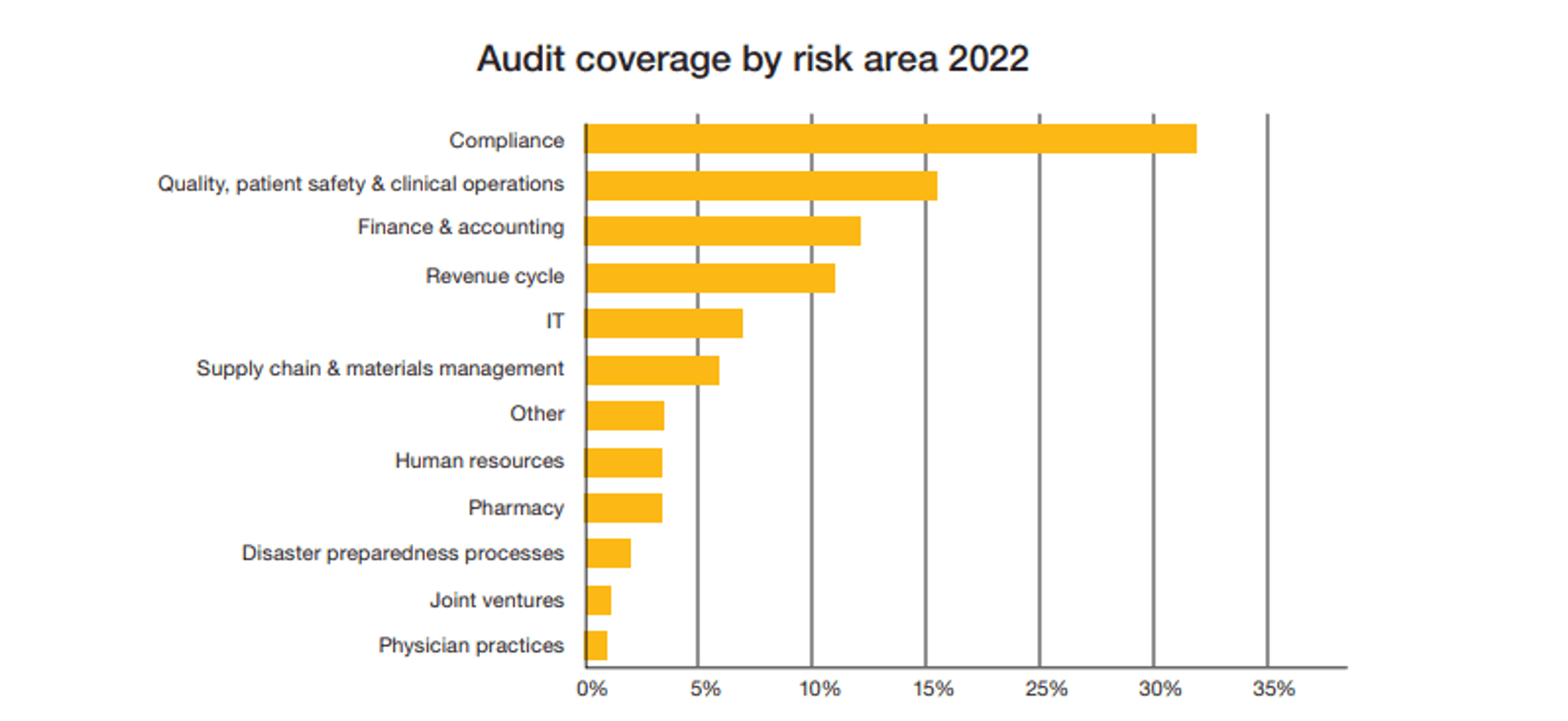
Image Source
Several key regulations form the backbone of healthcare regulatory compliance:
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA)
Enacted in 1996, HIPAA sets the standard for protecting sensitive patient data. Healthcare providers and their business associates must ensure that all the required physical, network, and process security measures are in place and followed to safeguard patient information.
Affordable Care Act (ACA)
The ACA, passed in 2010, introduced significant changes in health insurance. It includes provisions to expand Medicaid, protect patients with preexisting conditions, and implement health insurance exchanges, impacting how healthcare providers administer care and bill for services.
Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act (HITECH)
This act, passed in 2009, HITECH promotes the adoption and meaningful use of health information technology. It specifically addresses the privacy and security concerns associated with the electronic transmission of health information, partly by strengthening the enforcement of HIPAA rules.
The Role of Regulatory Bodies in Healthcare Compliance
Regulatory bodies play a crucial role in shaping and enforcing healthcare compliance. In the United States, key regulatory agencies include:
- The Department of Health and Human Services (HHS): Oversees the implementation of healthcare laws, including HIPAA and ACA.
- The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS): Administers the nation’s major healthcare programs and sets standards for healthcare providers and facilities.
- The Food and Drug Administration (FDA): Regulates the safety and efficacy of medications, medical devices, and other health-related products.
These agencies not only establish regulations but also monitor compliance, investigate violations, and impose penalties for non-compliance. Their guidance is crucial for healthcare providers to navigate the complex landscape of healthcare regulations effectively.
Healthcare regulatory compliance is a multifaceted and dynamic field, essential for maintaining the integrity and quality of healthcare services. Understanding and adhering to the regulations set by these bodies is not just a legal obligation but a fundamental component of providing safe and effective healthcare.
Challenges in Healthcare Regulatory Compliance
Healthcare regulatory compliance is a critical yet challenging aspect for healthcare providers and organizations. The complexity and ever-evolving nature of healthcare laws and regulations present several challenges that can impact the efficiency and effectiveness of healthcare delivery.
Some of the most common healthcare regulatory challenges include:
Keeping Up with Changing Regulations
Healthcare laws and regulations constantly evolve. Keeping up with these changes and understanding how they apply to specific healthcare practices can be daunting for providers.
Resource Allocation
Implementing and maintaining compliance requires significant resources, including time, personnel, and finances. Smaller practices, in particular, often struggle with allocating sufficient resources to compliance activities.
Training and Education
Ensuring all staff members are adequately trained on compliance issues is a continuous challenge. As regulations change, ongoing education and training become necessary to maintain compliance.
Data Management and Security
With the increasing digitization of health records, maintaining the security and privacy of patient data as per HIPAA and other regulations is a significant challenge. This includes protecting against data breaches and ensuring secure data handling practices.
Compliance Across Multiple Jurisdictions
For healthcare organizations operating in multiple states or countries, compliance becomes even more complex due to varying regional laws and regulations.
The Importance of Robust Healthcare Compliance
Non-compliance can have severe consequences for healthcare entities, including financial penalties, legal repercussions, damage to an organization’s reputation, and operational disruption.
For example, if a hospital system experiences a breach due to inadequate cybersecurity, it can expose thousands of patients’ personal information, leading to HIPAA violations and hefty fines. If a healthcare provider is found guilty of billing fraud or overcharging for services (intentional or not), both financial and legal penalties can ensure. Failure to keep up with operating licenses can lead to closures.
These challenges and examples highlight the importance of robust healthcare compliance strategies. Key steps to implementing solid compliance measures include:
Establish a Compliance Program
Develop a comprehensive compliance program that includes policies, procedures, and guidelines aligned with current healthcare regulations. This program should be tailored to the specific needs and risks of the organization.
Appoint a dedicated compliance officer and form a committee responsible for overseeing the compliance program. This team should have the authority and resources to enforce compliance standards effectively.
Adopt the Right Tools to Support Your Program
The speed and scale at which all businesses operate today—including healthcare organizations—requires the support of software tools that can automate and systematize processes, while managing data and keeping it secure. The market for healthcare compliance software is fast on the rise as organizations aim to improve and enhance their strategies.
Between 2024 and 2032, the market will nearly triple to reach more than $9BOpens in a new tab, underscoring the criticality of adopting a software-driven approach sooner rather than later.
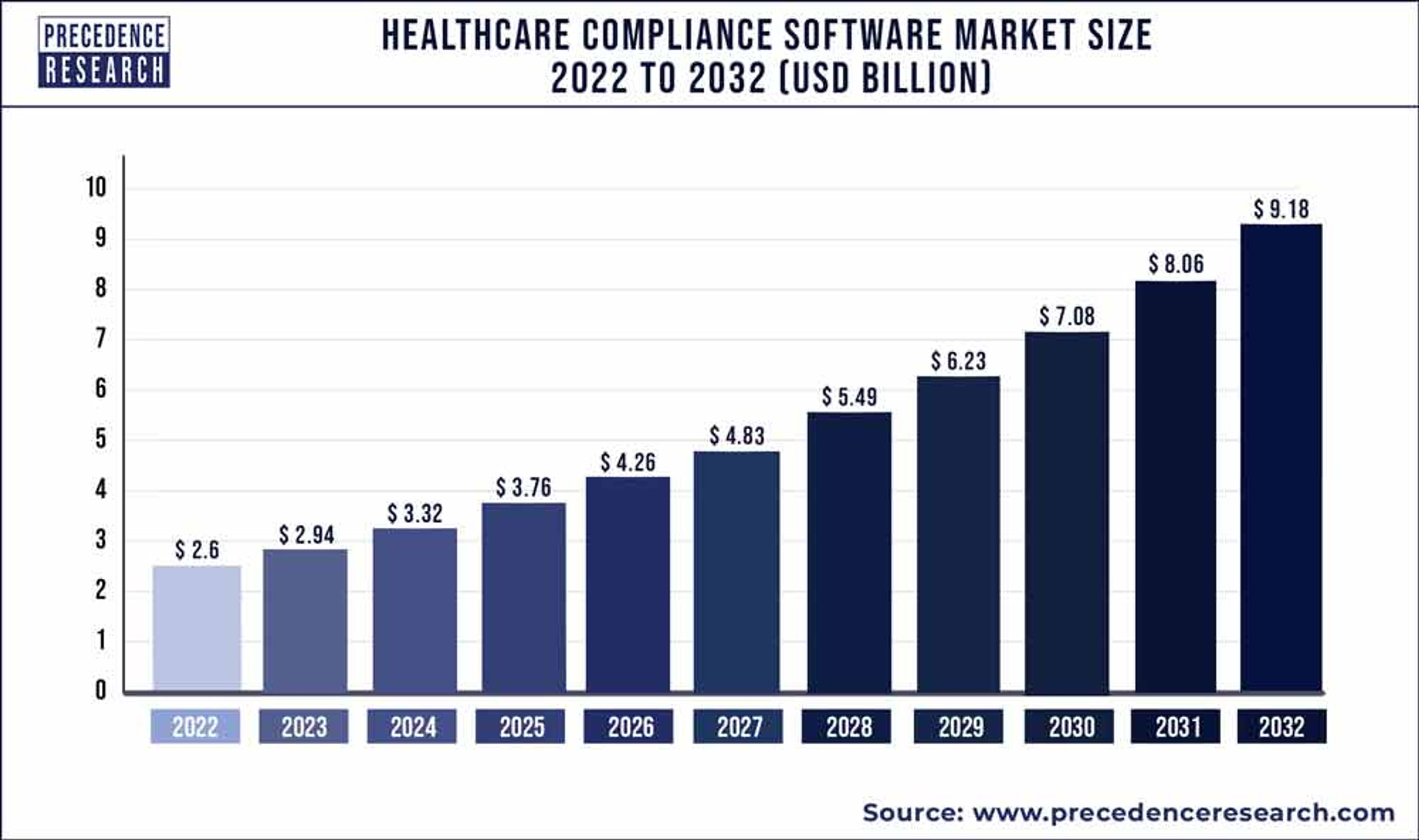
Image Source
Conduct Regular Risk Assessments
Regularly assess the organization for compliance risks. This includes evaluating the effectiveness of current compliance practices and identifying areas where improvements are needed, then developing action plans to make those improvements.
Implement Training and Education Programs
Unfortunately, many compliance risks—specifically those that are security related—happen due to unintentional internal issues. One report found that a staggering 96% of data breachesOpens in a new tab, for example, were caused by human error, and 24% by employee negligence or unawareness.

Image Source
It’s essential to ensure that all staff members receive ongoing training on compliance-related topics. This training should be updated regularly to reflect changes in regulations and organizational practices, well documented for clarity, and made easily accessible to employees at all times.
Effective Communication Channels
Establish clear channels for communicating compliance information throughout the organization. This includes regular and direct updates on regulatory changes, as well as open lines for reporting compliance concerns or violations.
Regular Auditing and Monitoring
Conduct periodic audits to verify compliance with regulations and the effectiveness of the compliance program. Monitoring should be both proactive and reactive, addressing potential issues before they become problematic. This should ideally be done using a software tool that can automate the process and deliver actionable insights in an ongoing way.
Responsive and Corrective Action Plans
Develop procedures for responding quickly and effectively to compliance violations. This includes investigating reported issues, taking corrective actions to address violations, and making necessary adjustments to prevent future occurrences.
Data Management and Security
Data is at the foundation of the way modern healthcare organizations operate. That means it’s also one of the key components to strong healthcare compliance. It’s imperative to implement robust data management systems, governance frameworks, and security measures that protect patient privacy, ensuring compliance with data protection regulations.
Stay Informed and Adaptive
Keep abreast of changes in healthcare laws and regulations. Adapt the compliance program as necessary to stay aligned with evolving legal requirements and best practices.
Foster a Culture of Compliance
Encourage a workplace culture that values and prioritizes healthcare compliance. This involves leadership demonstrating a commitment to ethical practices and compliance, and encouraging staff to take an active role in compliance efforts.
By taking these steps, healthcare organizations can build a strong foundation for compliance, mitigating risks and ensuring that they provide safe, legal, and high-quality care. Robust healthcare compliance is not just about avoiding penalties; it’s about committing to the highest standards of care and ethics in the healthcare industry.
Gaine provides ecosystem-wide software solutions designed specifically for healthcare and life sciences organizations. Our solutions improve patient outcomes, reduce administrative overhead, and ensure regulatory compliance at a lower overall cost. Learn more here about how Gaine can help to transform your compliance practices.